benedict's test colors|Benedict’s Test : iloilo Benedict’s solution is a deep-blue alkaline solution used to test for the presence of the aldehyde functional group, – CHO. One litre of Benedict’s solution can be prepared from 100 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate, 173 g of sodium citrate and 17.3 g . Tingnan ang higit pa Key Takeaways. Arnis is the national martial art of the Philippines. It emphasizes weapon-based fighting, particularly with sticks.; Arnis incorporates both offense and defense techniques. The art form has a deep cultural significance in Filipino society.; Arnis has gained global recognition and the admiration of famous martial artists.
PH0 · The Benedict's Test for Reducing and Non
PH1 · Benedict’s test: Definition, Principle, Uses, and Reagent
PH2 · Benedict’s Test
PH3 · Benedict’s Test
PH4 · Benedict's reagent
PH5 · Benedict's Test: Principle, Requirements, Procedure
PH6 · Benedict's Test : Principle, Reagent Preparation, Procedure and
PH7 · Benedict's Test : Principle, Reagent Preparation, Procedure and
PH8 · Benedict's Test
PH9 · 2.3: Simple Carbohydrates
Download the Walo88 app for an immersive gaming experience on your mobile device Download. Walo88 App: Download and Play Anytime, Anywhere! World’s best integrated entertainment native APP, providing a smooth and perfect user experience. Massive sports, top e-sports events, live dealer, slots, lottery and electronic games are all in the palm .
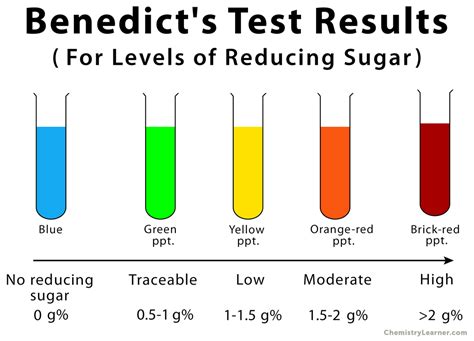
benedict's test colors*******If the color upon boiling is changed into green, then there would be 0.1 to 0.5 percent sugar in solution. If it changes color to yellow, then 0.5 to 1 percent sugar is present. If it changes to orange, then it means that 1 to 1.5 percent sugar is present. If color changes to red,then 1.5 to 2.0 percent sugar is . Tingnan ang higit paWhen Benedict’s solution and simple carbohydrates are heated, the solution changes to orange red/ brick red. This reaction is caused by the reducing property of . Tingnan ang higit paBenedict’s solution is a deep-blue alkaline solution used to test for the presence of the aldehyde functional group, – CHO. One litre of Benedict’s solution can be prepared from 100 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate, 173 g of sodium citrate and 17.3 g . Tingnan ang higit pa
Mar 9, 2022 — Any change in color from blue to green or yellow or orange or red within 3 minutes indicates a positive Benedict test i.e. presence of reducing sugar in the sample. For .To test for the presence of monosaccharides and reducing disaccharide sugars in food, the food sample is dissolved in water and a small amount of Benedict's reagent is added. During a water bath, which is usually 4–10 minutes, the solution should progress through the colors of blue (with no reducing sugar present), orange, yellow, green, red, and then brick red precipitate or brown (if a high concentration of reducing sugar is present). A color change would signify the presence o.
Nob 11, 2020 — Benedict’s test is performed by heating the reducing sugar solution with Benedict‘s reagent. The process of shifting of a hydrogen atom from one carbon atom to another in alkaline condition to produce enediols is known .What is Benedict’s Test? Benedict’s test is a chemical test that can be used to check for the presence of reducing sugars in a given analyte. Therefore, simple carbohydrates containing a .Mar 7, 2022 — Quality Checking: Benedict’s solution is blue in color. In order to check purity of Benedict’s solution take 5 ml of Benedict’s solution in test tube and heat it. If is does not .The Benedict’s test for non-reducing sugars: - Heat the test sample with dilute hydrochloric acid. Neutralise the test sample by adding sodium hydrocarbonate. Heat the test sample with .Benedict’s test is performed by heating the reducing sugar with Benedict‘s reagent. The presence of the alkaline sodium carbonate converts the sugar into a strong reducing agent called enediols. During the reduction reaction, the .We can test for the presence of simple carbohydrates such as glucose by using Benedict’s reagent. When simple carbohydrates are present, the Benedict’s reagent will change color .May 12, 2024 — Benedict’s test relies on the ability of reducing sugars to reduce cupric ions (Cu²⁺) present in Benedict’s solution, resulting in a color change from blue to green, yellow, orange, or even brick-red, depending on the amount .
May 12, 2024 — Benedict’s test relies on the ability of reducing sugars to reduce cupric ions (Cu²⁺) present in Benedict’s solution, resulting in a color change from blue to green, yellow, orange, or even brick-red, depending on the amount of .
Method. Add Benedict's reagent (which is blue as it contains copper (II) sulfate ions) to a sample solution in a test tube . It is important that an excess of Benedict’s solution is used so that there is more than enough copper (II) sulfate present to react with any sugar present; Heat the test tube in a water bath or beaker of water that has been brought to a boil for a few minutes
Peb 20, 2024 — Benedict’s Test is a chemical test used to identify reducing sugars present in the solution. Reducing sugars are those sugars that have reducing properties. All monosaccharides and disaccharides (apart from sucrose) are reducing sugars, such as glucose, fructose, lactose, etc; they contain an aldehyde (-CHO) or a ketonic C = O. Benedict’s Test also called .Dis 12, 2020 — The main contribution of Benedict’s reagent was the rapid detection of reducing sugars by color change, using stable alkaline agents that were not very corrosive. 7 While initially the method only indicated the presence or absence of glucose in a test sample, later, Benedict himself proposed a modification to make it semi-quantitative .Benedict’s TestMar 7, 2022 — Quality Checking: Benedict’s solution is blue in color. In order to check purity of Benedict’s solution take 5 ml of Benedict’s solution in test tube and heat it. If is does not change color, it means it is pure. Procedure of Benedict’s Test. Pipette 5 ml of Benedict’s reagent in a test tube (20x150mm).The Benedict’s test for reducing sugars: - Heat the test sample with Benedict’s Reagent. Observe the colour change. A brick red precipitate indicates the presence of a reducing sugar. The Benedict’s test for non-reducing sugars: - Heat the test sample with dilute hydrochloric acid. Neutralise the test sample by adding sodium hydrocarbonate.
Serial dilutions. Serial dilutions are created by taking a series of dilutions of a stock solution. The concentration decreases by the same quantity between each test tube. They can either be ‘doubling dilutions’ (where the concentration is halved between each test tube) or a desired range (e.g. 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 mmol dm-3); Serial dilutions are completed to create a standard to .We can test for the presence of simple carbohydrates such as glucose by using Benedict’s reagent. When simple carbohydrates are present, the Benedict’s reagent will change color from blue to orange-red when heated. We will be testing several substances for simple carbohydrates using this reagent.

Educational Purposes: This test is commonly used as a teaching tool in high school and college chemistry classes to demonstrate the principles of oxidation-reduction reactions and the specificity of chemical tests. History of Benedict’s Test. Benedict’s test is a commonly used method for detecting the presence of reducing sugars in a given .benedict's test colorsEducational Purposes: This test is commonly used as a teaching tool in high school and college chemistry classes to demonstrate the principles of oxidation-reduction reactions and the specificity of chemical tests. History of Benedict’s Test. Benedict’s test is a commonly used method for detecting the presence of reducing sugars in a given .The Benedict's test is a simple chemical test that can be used to check for the presence of reducing sugars. Reducing sugars are sugars that have free aldose or ketose groups capable of donating electrons to other molecules by oxidizing them. . The original color of Benedict's reagent is blue. It turns green, yellow, orange or red, depending .
Benedict's test is a test for the presence of monosaccharides or certain disaccharides in a solution. When a solution containing these sugars is mixed with Benedicts reagent and heated, a reduction reaction causes the .6. Add 3ml of Benedict’s solution to each of the test tubes. Make sure the dropper does not touch the test solution. 7. Note the colour of the samples in the table overleaf. 8. Place all of the test tubes in the waterbath/beaker of water for 5 minutes. 9. Carefully remove the tubes and, on the table overleaf, note the colours and if any solid wasPeb 20, 2024 — Benedict’s Reagent Test Result. The color change observed after performing Benedict’s test indicates the presence and concentration of reducing sugars. A positive result is indicated by the formation of a reddish-brown precipitate, which indicates a high concentration of reducing sugars. On the other hand, a negative result is indicated by .2 days ago — Take a look at the image of the benedict’s test colours of Benedict’s reagent that change from clear blue to brick-red and which are triggered by the exposure to reducing sugars. (Image will be Uploaded soon) Benedict’s test can also be used for checking the presence of glucose in a sample of urine. Since this benedict test for urine .benedict's test colors Benedict’s TestSet 10, 2021 — Benedict’s reagent is the indicator we use to detect monosaccharides. When monosaccharides are mixed with Benedict’s and heated, a color change occurs. If there is a small amount of monosaccharide in the solutions, a greenish solution is produced. If the solution contains a large amount of monosaccharide, an orangish precipitate results.Set 15, 2017 — When Benedict's Reagent finds an aldose (a sugar with an aldehyde group), it can oxidize the aldose to a carboxylic acid. For example: Since D-Glucose is oxidized, Cu is reduced to a red precipitate ($\ce{Cu2O}$). The colors range form green to red because the original Copper Citrate ($\ce{C6H8Cu2O7^4+}$) is blue in color. Source: QuoraMay 4, 2022 — Procedure of Benedict’s Test. Take 1ml of sample in a dry test tube. Take 1ml of 5% glucose and 1ml distilled water in two separate dry test tubes. Add 2ml of benedict’s reagent to all the test tubes. The test tubes are placed in a water bath for about 5 minutes. The development of the brick red color precipitate indicates a positive result.
Benedict's Reagent: A Test for Reducing Sugars Carbohydrates are divided into two groups based on the complexity of their structure. Simple carbohydrates can form either a single ring structure (monosaccharides) or a double ring structure (disaccharides -- formed when a pair of monosaccharides bond).Simple carbohydrates include familiar sugars such the .
The Aviator stats, generated by the Aviator game algorithm, are represented graphically, providing a visual interpretation of data. This representation aids in understanding the frequency of certain strategies and their corresponding results. The Aviator patterns, when further scrutinized, can even hint at possible future outcomes.
benedict's test colors|Benedict’s Test